Last Updated on October 30, 2024 by Owen McGab Enaohwo
It’s 24 hours to the launch of your biggest client’s product. All is set except for the final testing. The product tester has just called in sick—he has been taken to hospital and is unsure when he’ll be discharged.
There’s confusion in the office because no other employee knows how to conduct the test. The client is calling to get an update. If you had a knowledge base, any other staff would have been able to perform the testing by following documented instructions and save everyone the trouble.
SweetProcess simplifies the creation and management of knowledge bases to make employees and customers self-sufficient. Sign up for a 14-day free trial—no credit card needed.
Table of Contents
Why You Need a Knowledge Base for Your Business
Components of a Knowledge Base
How to Build a Knowledge Base From Scratch
How to Build a Knowledge Base Using SweetProcess
7 Knowledge Base Examples From Which You Can Learn
Knowledge Base Software and Tools
What to Consider Before Choosing a Tool to Manage Your Knowledge Base
Drive Operational Excellence With Knowledge Bases
What Is a Knowledge Base?

A knowledge base is a source of information, so a person who others go to for information technically qualifies as one. The concept of a knowledge base has existed since the beginning of socialization. There are usually people others seek information from because those people are well-informed.
Still, they may only sometimes be available when needed. This brings a major factor of knowledge bases to the fore: accessibility.
Having stationary knowledge bases seemed better than relying on humans due to accessibility. Microsoft Word and Google Docs are popular tools among first-time knowledge base users, but in the long run, these tools could be more effective as users need help with updating and organizing the documents in them.
A knowledge base is a resource containing information about an entity, particularly an organization. Such information includes business policies, standard operating procedures, and regulatory requirements. Information in a knowledge base must be authoritative because it’s the standard for the organization. Implementing knowledge base gatekeepers is vital to ensure that its content is solid.
Accessibility is a prerequisite for a knowledge base. Team members must be able to retrieve information from the knowledge base at any time. Considering how employees and stakeholders will engage with the knowledge base helps in building a system that they will find useful.
Why You Need a Knowledge Base for Your Business
The daily running of a business boils down to information—how well your staff understands the business and implements that knowledge in delivering your services. If you assign a task to two employees and you give one of them information on how to perform the task, leaving the other one with nothing, the person with the information will most likely perform better. Other benefits of having a knowledge base include the following:
Consistency and Standardization
Consistency is an attribute successful businesses use to remain relevant in the market. Take McDonald’s for instance. Their products are the same all over the world because they make use of the same recipe. Customers who walk into any of their branches can rest assured of getting products with the same taste because the staff uses the same recipe and other operational information regardless of their location.
A knowledge base provides your team with the same information so they can execute tasks uniformly. Changes in operations are reflected in the knowledge base to maintain consistency.
Saves Money

Although training is important in the workplace for employee efficiency, it takes up a chunk of an organization’s budget. You don’t have to stop training your employees, but you can reduce costs by shortening the training with a knowledge base. The goal is to empower team members with the right information. Documenting your business processes effectively in a knowledge base speeds up the employee onboarding process and enables them to perform tasks without undergoing weeks or months of training.
A knowledge base also saves costs by preventing damages and losses incurred from teammates performing tasks they aren’t knowledgeable about. Grievous mistakes from employees’ lack of knowledge could make a business fold up.
Compliance and Risk Management
One thing organizations dread the most is to come under the hammer of regulatory bodies due to non-compliance. It’s bad for any business as it shows their negligence to society in general. Non-compliance issues often stem from employees operating without proper guidelines. This can be avoided by documenting information in a knowledge base according to regulatory requirements.
Besides helping you stay compliant, an effective knowledge base also offers a basis for risk management. Team members avert operational risks and hazards better when they follow documented instructions to the letter.
Enhanced Employee Productivity
Productivity is a result of knowing what to do and doing it efficiently. When employees have access to work instructions, they swing into action immediately, wasting no time asking for information or waiting on someone else to guide them. Time wasted due to their lack of information reduces their productivity in the long run.
A knowledge base promotes and sustains productivity. If an employee seeks help from a colleague to execute a task, they become incapacitated when the colleague isn’t available to help them next time. However, with a knowledge base, they can always access the information they need and maintain high performance.
Competitive Advantage

Having a competitive advantage is about offering greater value to your customers and prospects. From an operational perspective, aligning your services with the latest demands in your industry keeps you ahead of your competitors.
Adopting a knowledge base enables you to update your documents to meet rising needs in your business and industry and implement these changes swiftly without obstructing your workflow.
Faster Scalability
Dealing with the increased demand that comes with scaling a business is challenging, especially as the pressure can reduce the quality of your service. Leveraging a knowledge base helps maintain good service across your organization as it grows. There’s no need to create new policies and procedures, as your growing team can access your knowledge base for any instructions. As you encounter new tasks, you can include instructions on how to execute them in the knowledge base, giving everyone instant access to the information.
Aids Self-Service and 24/7 Customer Support

Just as a knowledge base empowers employees to work independently, it also encourages customers to perform self-service by providing the details they need and guiding them through certain activities.
An example of a self-service knowledge base is the frequently asked questions (FAQs) page of a business website. It’s a good resource for uninterrupted customer support, as they can seek help at any time of the day. An eager customer who needs assistance in the middle of the night will be happy to get it on your self-service page instead of waiting until business opens in the morning.
Types of Knowledge Bases
There are two types of knowledge bases according to their user category and purpose: an internal knowledge base and an external knowledge base.
Internal Knowledge Base
An internal knowledge base is designed for an organization’s employees. It contains administrative policies and how-to instructions for executing tasks. If a team member wants to execute a task and can’t find the how-to guide in your internal knowledge base, it’s an opportunity to add that information to it.
The pieces of information in an internal knowledge base include:
- Company Policies
- Procedures and processes for various tasks
- How to onboard new employees
- How to apply for annual leave
- How to report sick
- How to file a complaint
- Forms and templates
- Compliance requirements
- How to use internal applications
Although the majority of information in a company knowledge base is meant for all team members, some items are for certain departments and staff, especially those in managerial roles. There’s a need to restrict such details to the specific audience with access controls so only authorized persons can access them.
The team at All Residential Real Estate, a property management company, used to rely on subject matter experts to facilitate its workflow, but that became a thing of the past when they built an internal knowledge base in SweetProcess. According to its managing director, Perry Beebe, this was a big win for the company.
“The biggest thing is that we no longer need to have subject matter experts. Previously, there would be a person who was an expert and would answer everybody’s questions. But that person may not be in the office at that point in time,” Perry says.
External Knowledge Base
An external knowledge base is a source of information for customers and other members of the public. Often referred to as a help desk, it’s available on the official website of a business. This knowledge base promotes self-service by answering users’ queries and offering instructions on how to resolve minor problems they may encounter in using the service.
The information available in an internal knowledge base includes the following:
- Subscription plans and billing
- Installation guide
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Troubleshooting guide
- Tutorials
- Copyright
- Privacy policy
- Account settings
As an educational institution, Belvidere Community Unit School District 100 must engage with its stakeholders in the best interest of its students. According to the organization’s quality assurance director, Sarah Brenner, their external knowledge base in SweetProcess is a great resource for keeping stakeholders updated about developments in the school.
“There’s a knowledge base function within the platform, and that’s a great way that all of our stakeholders—whether it be parents, staff, and especially some of our clerical staff who work a lot with our procedures—can access the information that they need,” Sarah says.
Components of a Knowledge Base
Creating a knowledge base aims to guide employees and customers with the right information. To achieve this, it must contain the following elements.
Articles/Documents
All the information in a knowledge base isn’t in a single document—there’s a document for each task. For example, if an employee needs to know how to create a client invoice, they will look for the document by typing the title in the system. As a team lead or manager, you can direct teammates to specific documents containing the information you want them to learn. Some knowledge base tools enable employees to sign off on documents they have read, providing evidence that they are knowledgeable about the subject.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

Frequently asked questions (FAQs) are must-haves for external knowledge bases. Every business has questions that people always ask. Answering these questions on the help desk or self-service page of your website reduces the number of queries you will receive from customers about them. When you answer all possible non-confidential questions about your business, customers will be well informed to make a buying decision without contacting you directly.
Community Section
Unlike the FAQs page, where you answer queries about your business, the community section allows users to interact about your products or services. A platform for user-generated content (UGC), people who are familiar with your offerings can share the customer experience journey and answer questions from others who are interested in your service or have encountered challenges using it.
The community section is an avenue to score some points and build your brand’s reputation, as it consists of real people who are usually not affiliated with your business.
How-to Guides
If an employee consults a knowledge base for information on how to perform a task, their best option is a how-to guide because it contains step-by-step instructions on how to perform a task from start to finish. A knowledge base is incomplete if this document is missing. How-to guides are most beneficial when they are concise with clear details of what the user needs to do at each point. To get the most out of how-to guides, make them multimedia by combining texts with other visual elements such as videos, images, charts, etc.
Search Functionality
Difficulty in finding documents is time-consuming and creates anxiety. This is what happens when using a knowledge base without search functionality—finding documents is a hassle. An effective knowledge base enables you to name documents and add unique tags to them for easy location. To retrieve a file, you simply enter its title or tag in the search bar.
Access Control
The ability to regulate access to content in your knowledge base is essential for protecting confidential information. A knowledge base offers admin access controls for determining the documents teammates can engage with. For security reasons, deploy the least privilege principle by granting users access on a need-to-know basis.
Notification System
A knowledge base is constantly changing with additional updates. Users must be aware of new inputs in the system as they make use of the content in their daily responsibilities, lest they implement outdated information. Notifying employees manually about every update is daunting, especially for large organizations. The right knowledge base notifies users subscribed to a thread about updates in real-time.
Importation
There are instances where you have existing knowledge base material, such as how-to guides, FAQs, or articles in external locations. A good knowledge base tool allows you to import the content into the system, saving time and resources you would have spent creating it from scratch. It also supports various file formats for seamless import.
How to Build a Knowledge Base From Scratch
It’s one thing to create a knowledge base, but deriving the intended value from it is a different ball game. Here are some tips to create a knowledge base that’s useful to your employees and customers.
Choose the Right Knowledge Base Platform
A knowledge base doesn’t exist in a vacuum but in a system. The first step to building one is to make the right choice. This decision can make or mar your results as you can only work with what the system offers. Check out what’s available on the market and conduct your research by reading articles like this for adequate information to make the right buying decision.
Define Your Goal

The goal of implementing a knowledge base may seem obvious: to empower your employees with the information they need to be efficient at their jobs. Contextualizing your goal gives you clear directions on how to achieve the best results. Look at what’s working for others, especially those in your field. If it works for them, it will most likely work for you. There’s a high chance you will find businesses in your industry that have recorded success stories from using SweetProcess as their knowledge base.
Identify Key Topics and Categories
Difficulties finding content in a knowledge base are a result of structuring problems. Outline the topics and categorize them based on their similarities. For an internal knowledge base, identify the relevant tags to use for each document. Ensure that the tags are unique to avoid having multiple results when you enter a particular tag in the search field. If you are creating a customer-facing knowledge base, grouping related articles helps users find more information easily. Arranging FAQs sequentially makes for informative reading.
Know Your Audience
The primary audiences of your internal knowledge base and external knowledge base are your employees and customers, respectively. Develop personas for both categories of people to better understand how to communicate with them. Using a language or tone that doesn’t fit their personas can lead to miscommunication and hinder understanding. This is especially true for creating external knowledge base content. A visitor to your website who struggles with understanding your language will exit.
Gather Information
Content in your knowledge base is the standard for operations in your organization and as such must be factual. There’s no room for assumption. Liaise with employees who perform specific tasks to get first-hand information on the best ways to execute those tasks. Test run the tasks if necessary to identify bottlenecks.
In creating an external knowledge base, speak with customer service agents to collect the most frequently asked questions and queries from customers. Providing that information in the help desk pages would reduce their queries.
Create and Format Content
Formatting the content in your knowledge base is just as important as having valuable information. Bear in mind that how-to guides are step-by-step instructions. Users should be able to get the directions they need easily. Formatting each piece of information in your knowledge base from scratch can be tedious. Adopt a system that offers various templates and forms to choose from.
Include multimedia
A multimedia knowledge base is less boring and engages users more. Determine the most suitable content format needed at each point. Would videos work better than text for capturing particular details? If that’s the case, make a video instead. Where it’s essential to show the progression of tasks, it’s best to use diagrams and charts.
Gather Feedback
It can be difficult to measure the effectiveness of a knowledge base until it’s operable. Encourage team members to share their experience of using the system after launching it. Use feedback forms to collect their opinions and address issues raised for smoother operations.
Regularly Update Content
A knowledge base begins to lose its relevance when it remains the same for long, and that’s because things are constantly changing in business. Failure to effect the rising changes in your knowledge base means its content will be dated, leading to adverse results when implemented.
Knowledge base management is key for preserving the usability of your knowledge base. Make it your responsibility to facilitate updates, or better still, appoint someone else for the role.
Ensure Accessibility
If a teammate needs to perform a task out of the office in the middle of the night, can they access the knowledge base for the information they need? Your knowledge base isn’t accessible if the answer is no. Getting this right entails adopting an application with cloud storage and remote access. Check your access controls regularly to ensure that employees have the right access to documents.
How to Build a Knowledge Base Using SweetProcess
SweetProcess is a knowledge management system for building knowledge bases. Its internal knowledge base software creates a level playing field in the workplace by decentralizing pieces of information that would ordinarily be privy to a select few, while its external knowledge base facilitates self-service to customers.
How to Create a Knowledge Base in SweetProcess
Click on “More” at the top of the page and then click on “Knowledge Bases.”
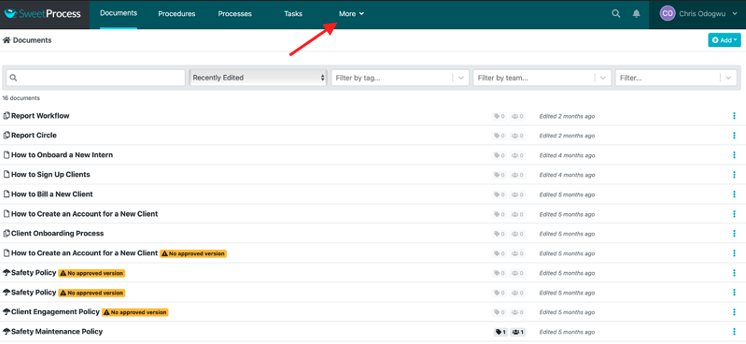
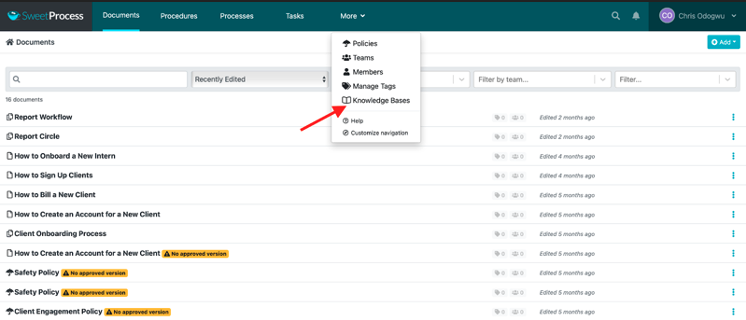
Click on “Create Knowledge Base.”
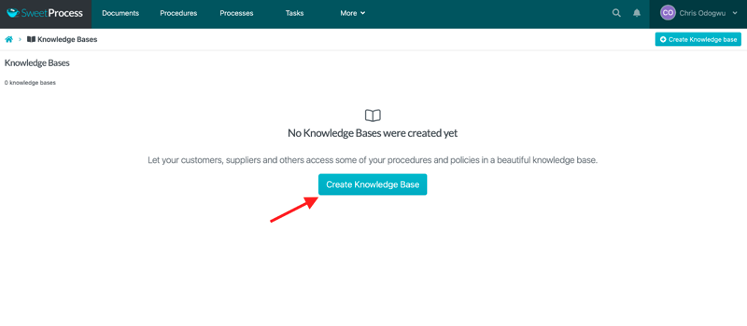
Enter the title of the knowledge base and click on “Continue.”
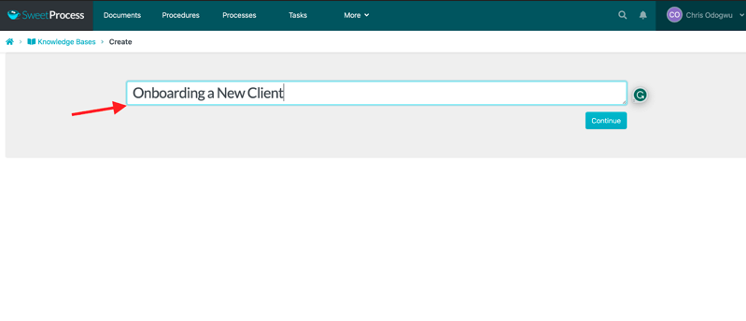
How to Create an External Knowledge Base in SweetProcess
Navigate to the knowledge base and click on the pencil icon beside the title.
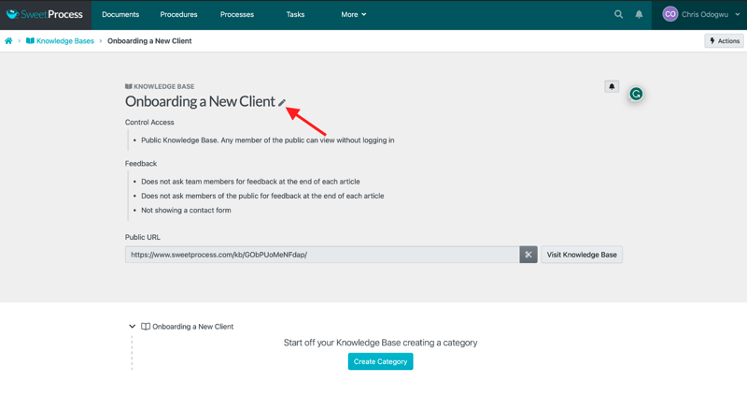
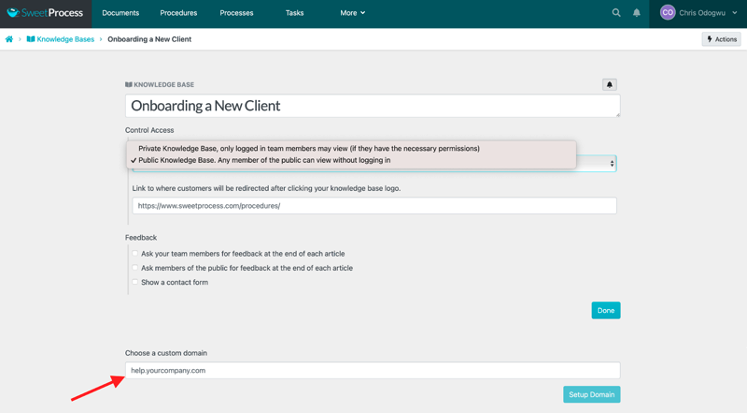
Click on the bar below “Control Access” and select “Public Knowledge Base. Any member of the public can view without logging in.”
Enter the URL you want customers to be redirected to when they click on the title of the knowledge base, as indicated below.
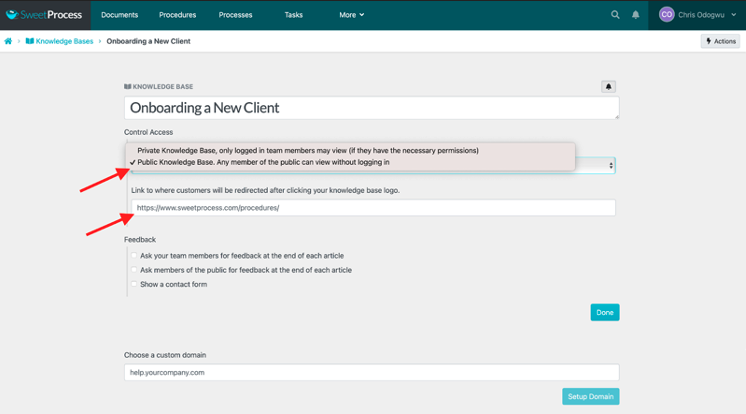
You can redirect customers to a custom domain if you want.
How to Create an Internal Knowledge Base in SweetProcess
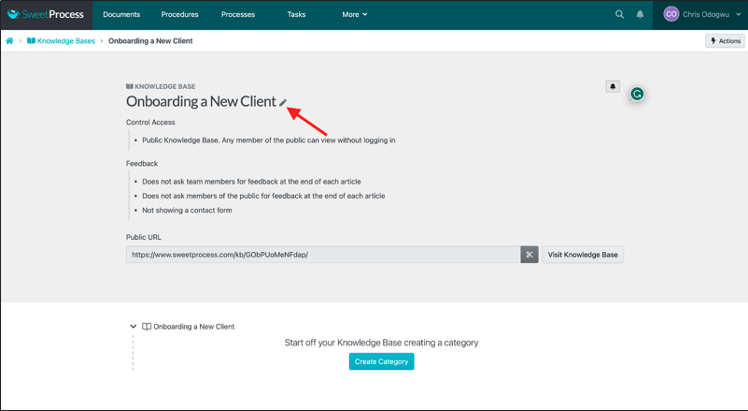
Navigate to the knowledge base and click the pencil icon beside the title.
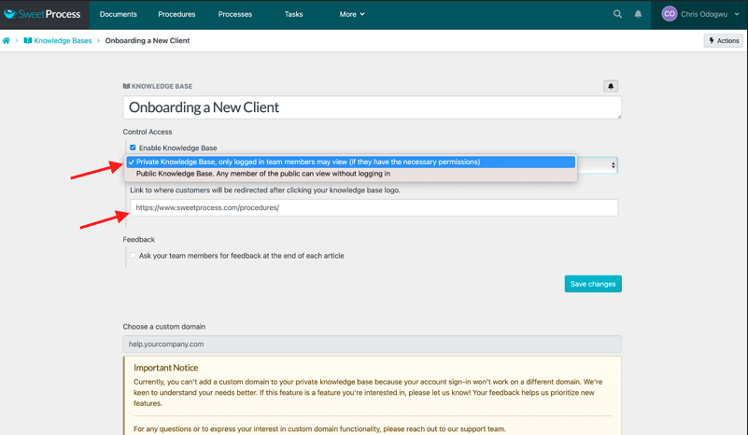
Click on the bar below “Control Access” and select “Private Knowledge Base, only logged-in team members may view (if they have the necessary permission).”
Enter the URL to which you want team members to be redirected when they click on the title of your knowledge base.
How to Manage Knowledge Bases in SweetProcess
Here’s how to get feedback or display a contact form on a knowledge base.
Click on “More” at the top of the page and then click on “Knowledge Bases.”
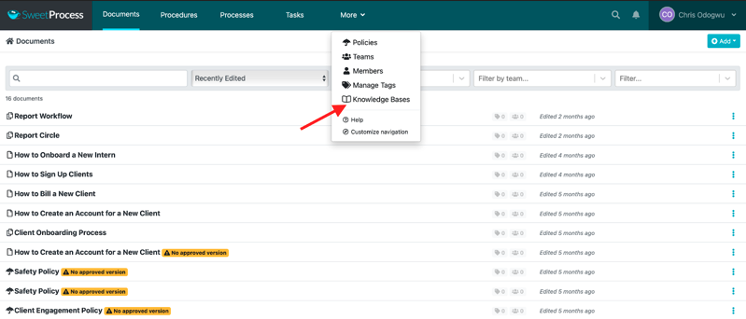
Click on the title of the knowledge base to open it.
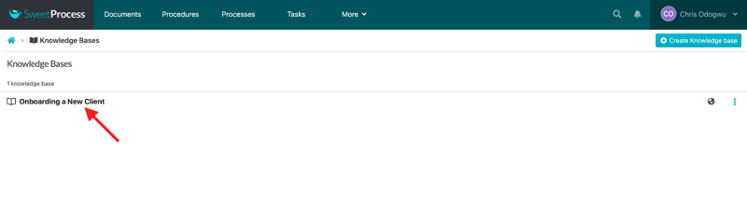
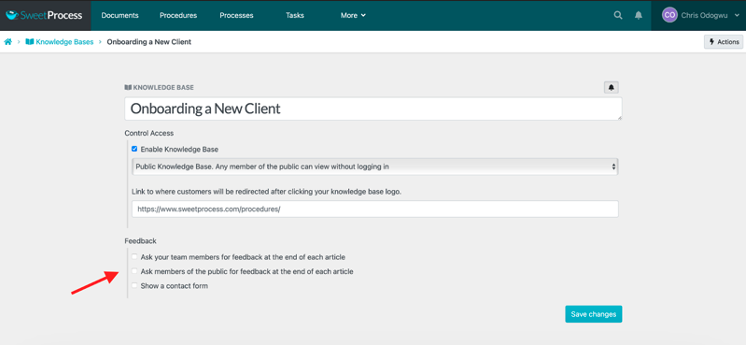
To get feedback from users or display a contact form, tick the appropriate box and click on “Save Changes.”
Here’s how to categorize your knowledge base:
Click on “Create Category.”
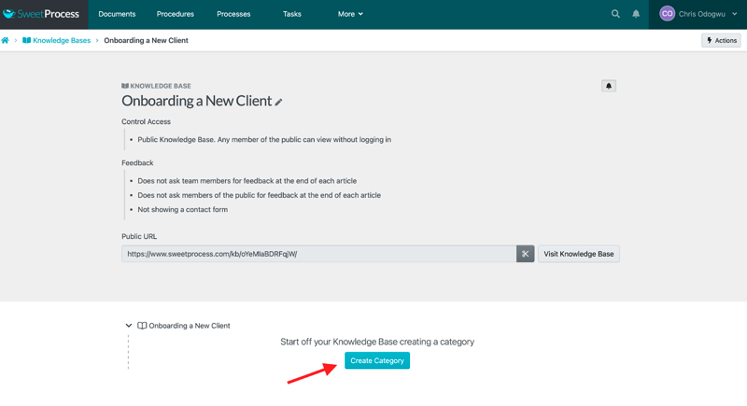
Enter the title of the category and click on the check icon.
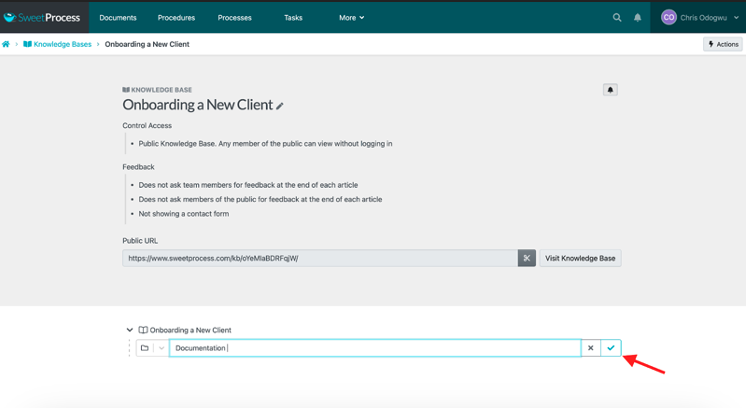
Click on the category.
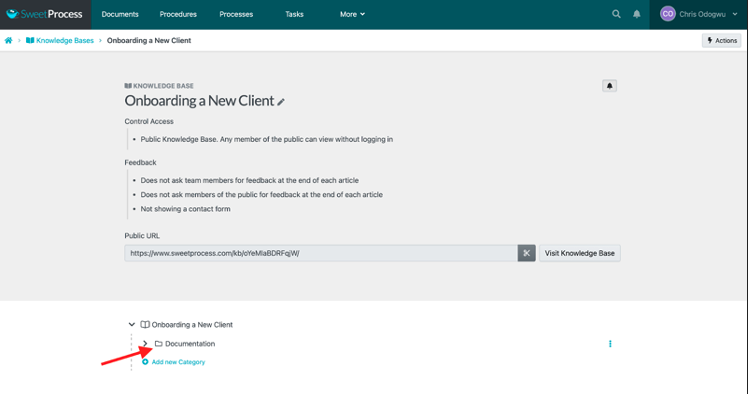
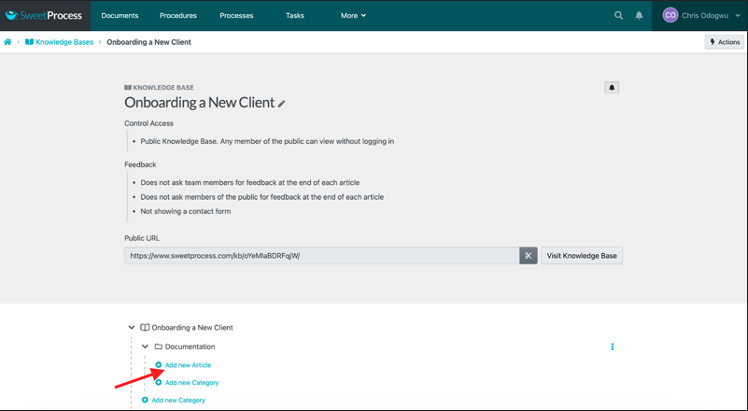
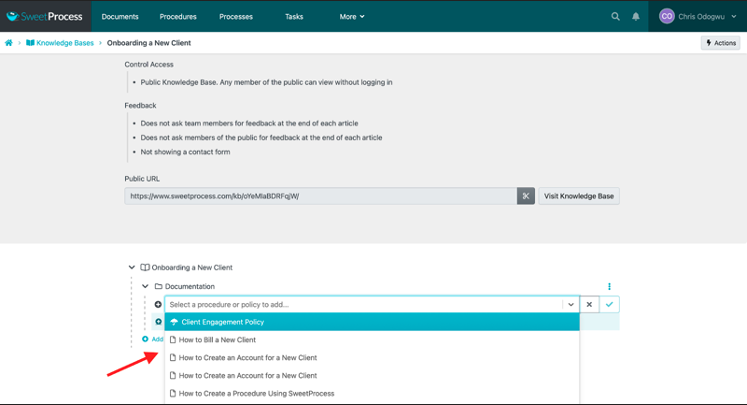
Click on “Add New Article” and select the article from the drop-down menu.
Jacob Syrytsia, chief executive officer at AEJuice, a video marketing agency, is one of the many entrepreneurs who have improved their business operations by building a knowledge base in SweetProcess. Jacob was able to take a vacation for the first time after implementing SweetProcess because he was confident that his employees could find whatever information they needed in the knowledge base.
“For every department, we have a separate knowledge base, and there’s a manager for each department. Either the manager or I keep it up to date. Whenever someone asks, ‘How do I use this tool?’ I just send them a link and it saves me about an hour of explaining,” Jacob says.
Ted Fogliani, CEO of e-commerce logistics company ShipCalm, believes in carrying his customers along, so he shows them how things are done in his company. He makes the most out of his knowledge base in SweetProcess by providing them with all the information they may need about his organization’s services.
“I want the customers to see what we’re doing. I want to make sure nothing’s been lost in translation, and so we have taken those processes and we have put them into the knowledge base section of SweetProcess to where our customers have access to that,” Ted says.
“Other things that we started using SweetProcess for is what we call need-to-know. Things that we want to ensure people are across, we actually put those communications into SweetProcess. Because it requests their sign-offs, we can see that they’ve seen it and read it.”
7 Knowledge Base Examples From Which You Can Learn
What exactly does a good knowledge base look like? Some brands have been able to create knowledge bases that meet their customers’ needs by providing relevant information that facilitates self-service. Here are examples of external knowledge bases you can take a cue from to build your own.
SweetProcess
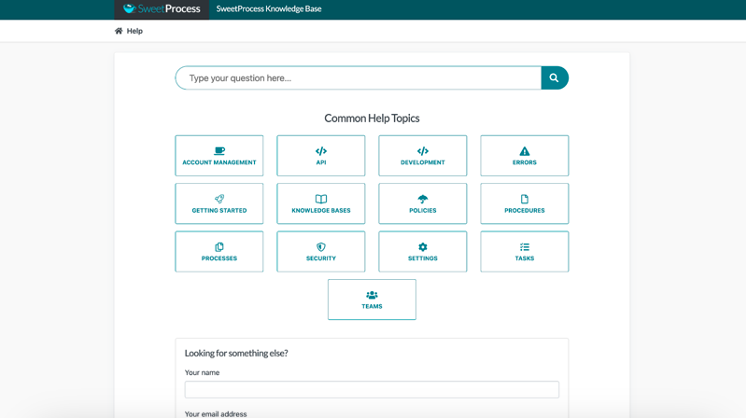
Knowledge management software like SweetProcess has a help page that serves as its external knowledge base. It offers thirteen topic categories, each one consisting of in-depth information for resolving user challenges.
If the information a user is looking for isn’t available on the page, there’s a contact form they can use to request it. When they aren’t sure of the category containing the information they need, there’s a search bar where they can enter specific queries and retrieve the most suitable information.
Wistia
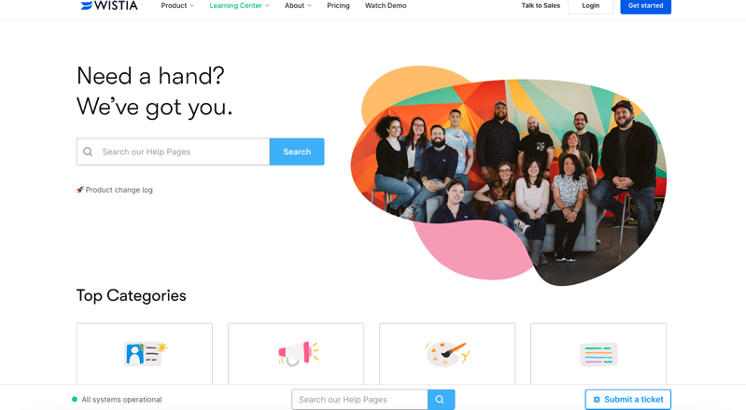
Video marketing platform Wistia offers an external knowledge base on its Learning Center page where it groups its help topics into four categories. A user who arrives on the page can click on the category that resonates with their inquiry to get the help they need quickly.
Underneath the categories are “Top Articles” that address common issues customers encounter. There’s also a search bar at the top that visitors can use to search for specific topics, especially when they aren’t sure of the category it fits in.
Bluehost
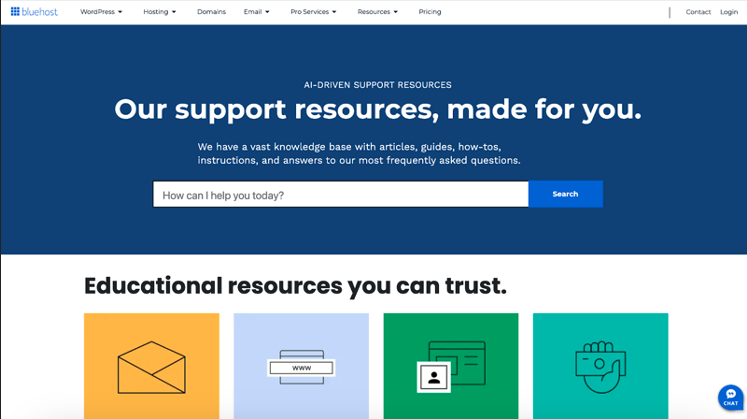
Web hosting service provider Bluehost has a knowledge base that contains four categories of help guides. Underneath the categories are articles on a wide range of topics that it claims are vital for everyday life. A user can dive right into the information they need by entering their query in the search bar at the top.
Hubspot
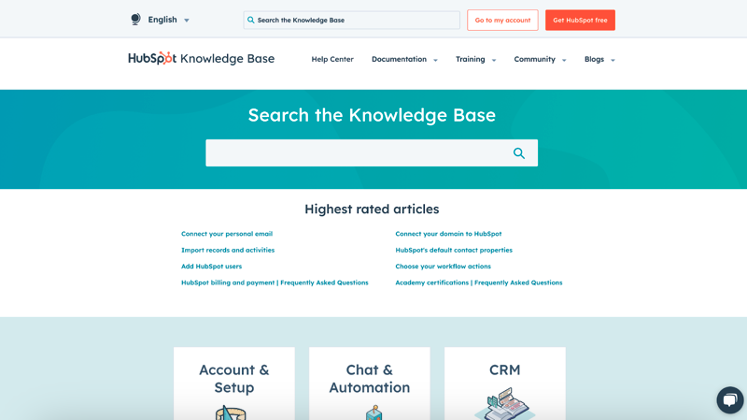
Customer relationship management (CRM) tool Hubspot offers an external knowledge base comprising ten help categories. It showcases the “Highest rated articles” that users may find most helpful in solving queries related to the platform. There’s also a “Search the Knowledge Base” feature they can use to search for information directly.
Stripe
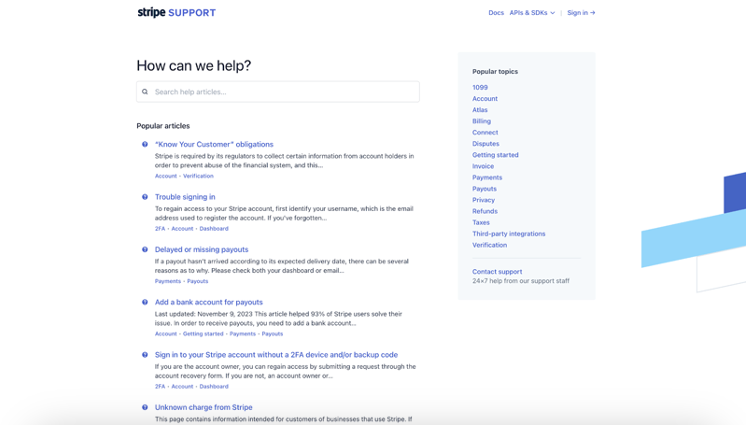
Financial services platform Stripe has a customer support page that showcases several articles on activities that customers may need help with. On the right side of the page are fifteen topic categories addressing queries that may arise from using the software. It simplifies access to information with a search bar at the top that users can use to retrieve specific data.
Semrush
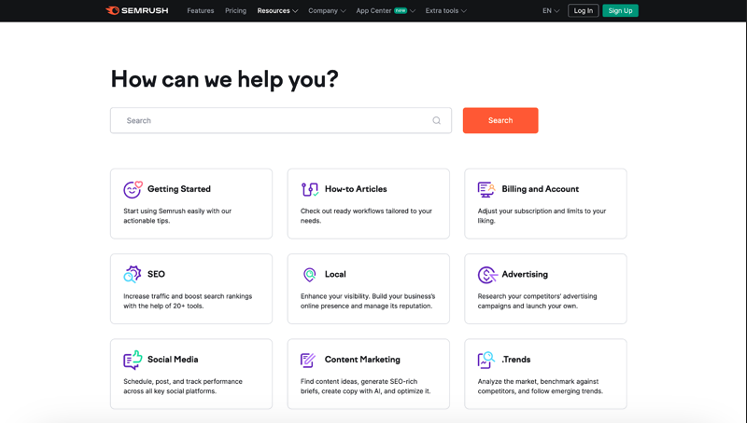
Online visibility management system Semrush offers a rich knowledge base with twelve help topic categories. Each category has information on related subjects and guidelines on how to resolve problems. It also adopts a search feature that allows users to access specific information directly and faster without going through the categories.
Buffer
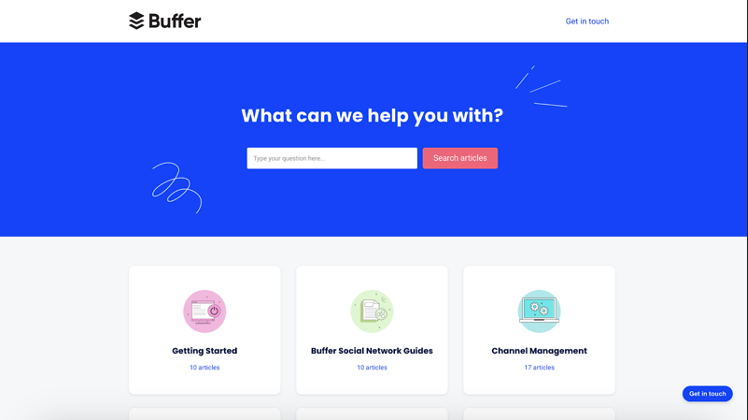
Social media management platform Buffer keeps its help center simple with fifteen topic categories and a search bar for retrieving information. As a user arrives on the page, they have the option of exploring each category to get the help they need or searching for specific content in the search bar.
Knowledge Base Software and Tools
A knowledge base software is an application for creating and managing information. It decentralizes information and offers remote access to authorized persons.
Every business has important information about its operations, including how to perform tasks. So, team members must work with the same information regardless of their location to maintain consistency in performance.
A knowledge base software streamlines the documentation and dissemination of information across an organization. It offers content creation tools to build content from scratch, update existing documents, and disseminate information to the right channels easily. Automation is a core feature of a knowledge base tool. This allows you to automate repetitive manual tasks in the information cycle, removing human bottlenecks that can slow down work.
The most effective knowledge base software offers cloud storage, allowing users to store and access information from any location without being confined to specific computer systems or physical locations. However, remote access poses higher security risks as cybercriminals have more opportunities to gain unauthorized access to data in cloud storage. To overcome this challenge, a knowledge base software must have strong security features including access controls, multi-factor authentication, and encryption.
What to Consider Before Choosing a Tool to Manage Your Knowledge Base
Implementing the right knowledge base software eliminates operational bottlenecks, enhances employee productivity, and facilitates customer satisfaction. To enjoy these benefits and more, you need to consider the following factors in your selection.
Scalability
The demand for your services increases as your business grows. A knowledge base that isn’t scalable won’t be able to accommodate your rising business needs and will clog your workflow. Ensure that your knowledge base tool can withstand more workload.
Cost
Cost is proportional to value in choosing a knowledge base software. Aim for an app with various subscription options. This allows you to choose the most suitable package for your business at different times, and you can upgrade your subscription to a higher plan as your business expands. Look out for available discounts to save some money. Many software platforms offer discounts when users subscribe to their annual plans.
Version History
Version history is a documentation feature for tracking updates to content in a system. It allows you to have various versions of a document for different purposes. Choosing a knowledge base software with this feature informs users about inputs made to a document and guides them in using the correct files in different scenarios.
Integration
There’s only so much you can achieve with one app. Using multiple apps makes for a smoother and more effective workflow. Integration enables you to put your favorite tools in one system instead of having them in different places. A knowledge base software that supports multiple integration is more valuable as it saves time and increases output.
Customization
Knowledge base tools are designed for a mass audience, but the most effective ones create room for users to customize them to their unique business environments. Confirm that the features embedded in the software can be adjusted to your needs to get the most out of them.
Ease of Use
User experience is a primary consideration in application design—the easier it is to navigate software and meet performance metrics, the higher the satisfaction rate. Simplicity is paramount. You should be able to set up, operate, and manage the knowledge base software with basic computer skills. Otherwise, you will encounter setbacks while using it.
Analytics and Reporting

A knowledge base software with reporting and analytics gives insights into current performances and provides data to make well-informed decisions. It also promotes employee accountability as you see how they engage with ongoing projects.
There aren’t many knowledge base software with all the above features. You hit the jackpot if you find one with them. We can confirm that SweetProcess offers all those features and more. Business intelligence and lean Six Sigma champion at Turkstra Lumber, Jamie Ramsden, utilizes SweetProcess to its full potential as a knowledge base. His teammates are confident in executing independent tasks by themselves because they can access the information they need, and when it’s time to collaborate, they have the resources to work collectively. “SweetProcess has to be something more than just a fancy way of writing down all the things you do, and that’s what it has managed to be. It’s a way that employees of all stripes can make corrections and participate,” Jamie says, and that’s because the system is equipped with the right features.
Set up your team for success by signing up for a 14-day free trial of SweetProcess without a credit card and confirm the features mentioned above for yourself.
Drive Operational Excellence With Knowledge Bases
“Now that we have SweetProcess, it’s the bible for us. Digital stuff can be quite complex. Even seasoned people who have been here for years still use SweetProcess. They go through the steps to make sure that they don’t miss anything or unnecessarily do something the wrong way. It’s really the bible for us now.”
These are the words of Dave Meindl, senior advisor of digital technology and performance at Mudd Advertising after he built a knowledge base with SweetProcess. An effective knowledge base should be the standard your organization operates by, and it takes great software to build that.
Do you want to enhance your business operations like Dave and the other entrepreneurs we have shared with you? SweetProcess is designed to assist you with that. You don’t need to create a knowledge base from scratch as it offers several knowledge base documentation templates you can adapt.
If you need help creating the knowledge base article, our Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool, SweetAI, can help you.
Sign up for a 14-day free trial without a credit card to achieve the success you desire.

